

With WebStorm, you can set the default system node alias as your project’s Node.js version. If the installation is missing, click and configure it as a local interpreter manually. If you followed the standard installation procedure, in most cases the required Node.js installation is on the list. On the Node.js page that opens, select the required Node.js installation from the Node Interpreter list. Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | Node.js.
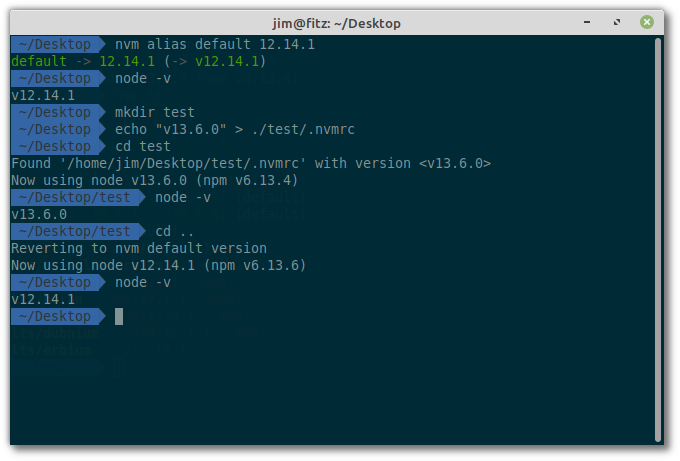
With WebStorm, you can have several installations of Node.js and switch between them while working on the same project. See Node.js with Docker, Node.js via SSH, and Node.js with Vagrant for details. To run a Node.js application remotely, configure it as a remote interpreter. In most cases, WebStorm detects Node.js installations, configures them as interpreters automatically, and adds them to the list where you can select the relevant one. If you want to switch among several Node.js installations, they must be configured as local Node.js interpreters.
#DETECT NODE JS MAC INSTALL#
If you follow the standard installation procedure, in most cases WebStorm detects Node.js itself.Īnd even if you have no Node.js on your computer, you can install it when creating a new Node.js application in the Create New Project dialog, see Creating a new Node.js application below. If you need Node.js only as a local runtime for your application or for managing npm packages, running JavaScript linters, build tools, test frameworks, and so on, just install Node.js.
WebStorm integrates with Node.js providing assistance in configuring, editing, running, debugging, testing, profiling, and maintaining your applications. Node.js is a lightweight runtime environment for executing JavaScript outside the browser, for example on the server or in the command line.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
